
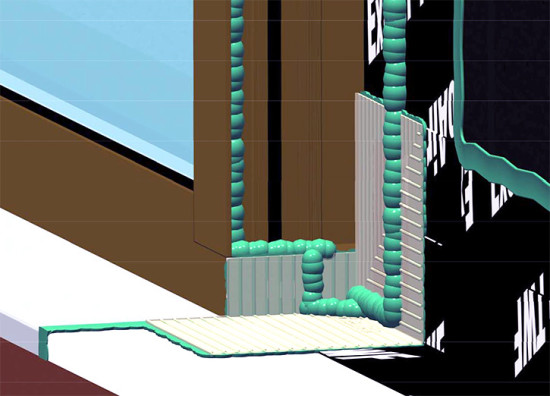
However, this technology needs a temperature differential between the inside and outside ambient temperatures Considerations Other abnormalities that may be detected are thermal bridging, insulation condition, and air leakage. Infrared images are analyzed to identify moisture issues from water intrusion, or interstitial condensation. Convective loops are when air moves within a wall or ceiling, and this can result in 10% to 20% of heat loss.īuilding envelope thermography includes the use of an infrared camera to view temperature anomalies on the interior and exterior surfaces of the building structure. Air control also includes the control of windwashing, cold air passing through insulation, and convective loops. It also consists of the airflow through components of the building envelope itself, as well as in and out of the interior space. The structure that performs this function is called the air barrier system. Control of air movement includes the flow of air through the enclosure. For more about weatherproofing envelopes, read here.Ĭontrol of airflow is vital to safeguard high indoor air quality, control energy consumption, avoid condensation, and to provide comfort. Basement waterproofing and proper drainage help keep the walls dry, and the building envelope may include a moisture barrier under the floor.


Moisture can easily enter basements through the walls or the floor. They rely on siding, and an underlayment layer referred to as housewrap. Typically, most materials will not remain sealed over the long term, and this system is minimal, but conventional residential construction generally treats walls as sealed-surface systems. Sealed-surface walls do not let water penetrate the exterior surface of the siding material. Types of barrier walls include concrete and some masonry walls. Barrier walls allow water to be absorbed but not to penetrate the wall. Drainage walls may also be ventilated to help with drying. Drainage walls let any water that may leak into the wall to drain out. Types of wall systems concerning water penetration are barrier, drainage, and surface-sealed walls. Walls do not receive the same level of water exposure as roofs but can still leak water. Residential roofs may also be ventilated to help eliminate moisture due to leakage and condensation. Pitched roofs are typically used for residential buildings and are covered with an underlayment material beneath the roof covering material as the second line of defense. The design of pitched roofs is to shed water but not resist standing water, which can happen during wind-driven rain or ice damming. Flat roofs slope up to 10° or 15° but are built to withstand standing water. Two broad types of roofs are flat and pitched. One of the primary purposes of a roof is to resist water. There are multiple strategies to defend against weather, namely, barriers, drained screens, and mass storage systems. The control function of a building envelope focuses, on rain control, air control, heat control, and vapor control. Finish functions mean meeting the desired visual aesthetics both on the inside and outside. Control functions include directing the flow of matter and energy of all types. Support functions are to resist and transfer structural and dynamic loads. The many functions of the building envelope fall into three categories: support, control, and finish. Building envelopes keep the conditioned air from escaping the building, cold air from getting inside a heated building, and help to minimize energy waste, while also controlling ventilation and airflow. Climate-controlled buildings need a shell that keeps the elements from affecting the inside air conditioning and heating systems that make interior conditions comfortable and safe. One of the crucial functions of a building envelope is to enable climate control. Building envelopes may also provide some aesthetic appeal with attractive finishes while maintaining the structure’s internal condition. Improving a structure’s envelope helps in protecting the building from the elements, supporting mechanical loads, and keeping the interior safe from outside hazards. A building envelope encompasses the building structure to shield it from damage.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
